What is SEO (search engine optimisation)?


SEO stands for ‘search engine optimisation’. In short, it's a service that improves your website visibility and trust online. The better the visibility of your pages in search results, for relevant keywords to your industry and business, the more traffic you will receive to your website, attracting either new or repeat customers.
Search engines, like Google, use bots (also known as spiders) to crawl website pages on the internet, storing the data they find and putting them into an index. Search engines have their own algorithms which take into account lots of different ranking factors or signals. This helps to determine the order in which pages should appear within search results, when different search terms are entered. In essence, websites rank higher when they can demonstrate trustworthiness and display content which is relevant to key search terms. The website pages which give users the clearest answer to their question, or provide them with the information most relevant to their search, will rank the highest. Optimising your website and content, showing a good understanding of the different areas of SEO, can help your pages to rank higher in search results.
There are a range of principles to be aware of around how different pages on your website will be deemed SEO-friendly. For example, the quality of your on-site content, meta data, crawlability and mobile-friendliness are just a few important factors in your site architecture.
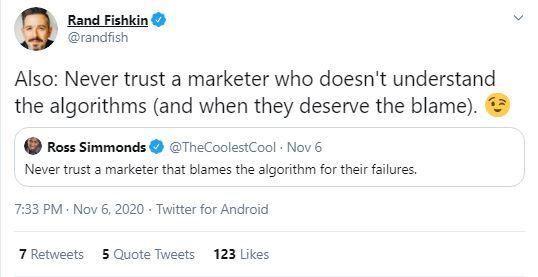
So, why should you care about what SEO does for your brand?
Do you want the short answer or the long answer?
Well, to put it in its most basic terms, good SEO produces measurable results for your website and business, which can get more people to notice you and increase your customer base, ultimately improving your brand’s reputation.
You can find more detail about how this works in the following sections. But here are some of the ways your brand can see an uplift from SEO:
The ultimate goal in SEO is to be more visible – we want your website to be in front of your target audience so that you get more traffic and sales. An important ranking factor is the trustworthiness of your domain. How much authority does your website have compared to competitors?
Ranging from 0 to 100, the higher your domain authority, the more likely your website is to appear in search results.
There are many different ways to improve the authority of your domain and we're going to list a few in this article.
Any good SEO professional will know how important it is to stay constantly aware of what their competitors are doing. Similarly, a strong SEO strategy starts with careful planning and research – competitor monitoring is high up on the list of priorities in these crucial early stages (and should form part of your regular BAU tasks too).
Up-to-date knowledge of competitor marketing activity, at all times, is valuable as it allows you to assess your position within search in relation to others in your field, identifying opportunities to surpass them and climb the rankings where necessary. Even if you were ranking at the top of Google for your target keywords, monitoring your neighbours in the search real estate is still essential, to help strengthen your position and be ready to take appropriate action if any sudden ranking drops occur.
There are many ways to research competitor activity, and motivations for doing so, which will be expanded on in this article. But here are a few popular and effective methods of competitor research:
Content is king. If your site doesn’t contain high-quality content which educates, entertains or inspires (or all three!), then your traffic won’t be engaged and you won’t retain them. Keeping users onsite for as long as possible is crucial, to get them to either convert or to keep coming back as repeat visitors, who build trust for your brand over time. Popular content formats now include blogs, videos, interactive content, infographics, podcasts, how-to guides, quizzes, polls and whitepapers.
Ideally, your content will be good enough to be shared online, so that your traffic, or other authoritative sites, can tell their followers/readers about how great you are and send a valuable trust signal to Google.
You can’t wait for this to happen though. It isn't enough to just create content and hope for the best, hoping it drives traffic, gets shares and, ultimately, results in leads or sales. This is where content marketing comes in. The process of content marketing is a combination of efforts to promote the content you have created.
Social share buttons on your page are, of course, an essential first step for allowing others to promote your content for free once you set it live. But there is so much more to it than this. You have to actually get them to your site first. There are a range of strategies you can use to market your content, get it seen by relevant search traffic and boost its SEO performance. You can read about them in more detail in further sections, but to summarise, content marketing for SEO has the following approaches at its core:
You should always make sure to plan your content strategies ahead of time, with the use of editorial calendars to help you properly prepare and keep an overall view of all activity. As well as being a place to schedule all of your ideas, headlines, and related activity, it can include timelines of execution for each team involved (design, copywriting, social, digital PR, etc). You can also create annual editorial calendars to ensure you harness opportunities to create content around key awareness days and events relevant to your industry. Many of these are on the same day every year, so there’s no excuse to miss out on the potential value of getting in on the conversation in a meaningful way, especially as journalists will create stories around these dates year in, year out.
If content is king, then it should be unique, right? Despite using a handy analogy to illustrate this point in a way that’s a bit jazzier than saying “don't copy content”, it is indeed true. Duplicate content is bad – who wants pretenders to the throne, after all? (Okay, we’ll stop with the regal imagery now.) Although duplicate content may not be bad practice in the way you might think (Google have confirmed there’s no definitive ‘duplicate content penalty’, per se, as popular misconception might have you believe), it will still hold you back from performing well in search.
If you were continuously creating large volumes of duplicate content in order to manipulate rankings (although if you’re really trying that in this day and age, good luck to you), then you may well find that Google decides to negatively index your site, which will not be good for your rankings.
However, sometimes duplicate content issues may occur unintentionally, for example if you have different URLs for a single page on your site, in order to support different devices. In this case, you can canonicalise your chosen pages to indicate which ones Google should index.
As the end of the day, Google needs to see expertise, authority and trust (EAT) in your site content in order to see it as high quality and indicate that you are a trustworthy brand. This ensures that businesses who spend time creating relevant, informative content for their specific target customers are quite rightly given precedence in rankings. So your content should be as unique as possible, presenting something original and of value to your site visitors, in return for them giving you their precious time by engaging with your site.
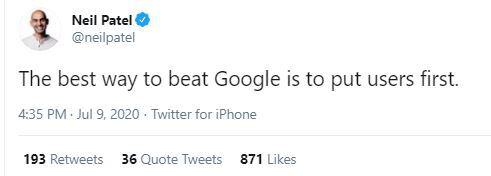
What is link building? In a nutshell, link building is the process of getting other websites to link back to your website. Every website needs these links (known as backlinks or inbound links), as they still have the potential to be highly impactful to your SEO performance. Increasing the number of high-quality backlinks to a webpage helps to achieve the goal of boosting search rankings. Having a strong, considered SEO strategy to build backlinks and drive referral traffic can also help to increase domain authority.
The reason that link building is effective is because backlinks from high-authority domains, within relevant industries, create trust signals for search engines. These signals help search engines to understand that your website is relevant to your targeted keywords. When credible third-party sites link to you, it has a positive influence on your website – passing some of their authority to your domain. Of course, the extra referral traffic you may receive is a bonus too, with its own positive effects on SEO.
There are ever-evolving rules of thumb to consider when creating target lists of sites you would like to gain backlinks from and the tactic you will use to target them. This isn’t like the old days of link-building, when quantity was pretty much all a website needed to see results. You can’t just gain endless links from as many sites as possible, in any way possible anymore, regardless of their relevance or authority (you'll definitely be penalised by Google for this spammy approach).
Joshua Hardwick, Ahrefs’ Head of Content, has kept this tweet pinned for over a year as the fact remains:
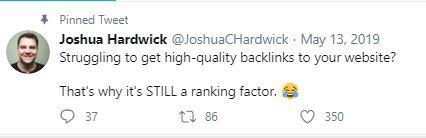
Ask yourself these key questions before you start link-building:
Your site should have a balanced mix of follow and nofollow links, as Google will see this as an indicator of properly-executed organic marketing activity for a ‘healthy’ website. Although follow links are the ideal outcome from strong target sites whose authority you’d like to be passed onto you, no website would want every link to be followed, as some are naturally-occurring, from sites you don’t want to pass their authority to you. It would also be highly unusual for every backlink to be a followed link, whether it’s from a reputable site or not, so Google would see this as suspicious.
Many SEOs will know the frustration of getting a journalist to link to their site only to find that the link is nofollow. This is becoming an increasingly common occurrence as many news sites have adopted blanket nofollow policies in order to protect their own site profile. Rightly or wrongly, they think it best to avoid the potential hazard of linking to a low-quality site and hurting their own site authority in Google (cue heated debate from SEOs around whether they are justified in doing this).
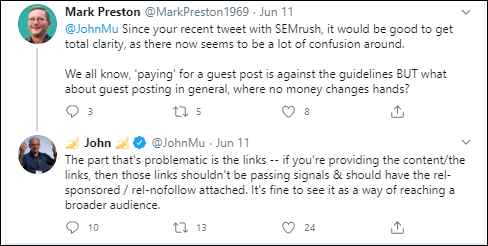
When deciding how you will acquire backlinks, look at your brand and stick to what works in your industry, what content has / hasn’t worked for you before, and what is interesting / relevant enough to get a response from your target sites. There are various methods which aren’t effective for organic SEO anymore, such as guest posts, which now have to be labelled as sponsored content. This is because any content you are providing yourself isn’t naturally-earned, so doesn’t deserve the passed authority from the referring website, as far as search engines are concerned. Google’s John Mueller explains this below.
When planning your content, consider linkable assets which can sit on a third-party site and gives them a reason they have to link back to you (more about this in the creative SEO campaigns section, below). These include videos, infographics, surveys and quizzes.
Remember that you don’t always have to create new content in order to gain backlinks. Effective SEO activity should incorporate regular BAU tasks such as:
Digital PR is an online marketing strategy used by businesses to increase their online presence. It involves networking with journalists, bloggers and influencers to gain high-quality backlinks and social media mentions to improve SEO.
Digital PR is similar in a way to traditional PR, but it offers the ability to reach a wider audience online – as well as a much more targeted audience, when needed. Online press releases, business profiling, building relationships with journalists and bloggers, influencer marketing, blogger outreach, blogs, content creation, thought leadership and creative content campaigns are all tasks that fall under digital PR.
The ultimate goal of digital PR is to help improve website reputation and increase brand visibility for a target audience. A successful digital PR strategy can grow website traffic, enhance SEO, generate leads or sales, improve brand image and reputation, and establish you as a thought leader in your industry.
Establishing yourself as a trusted authority in your industry, whose expertise is widely respected, can go a long way. Thought leaders are commonly asked to share their insight with relevant audiences, which can in turn gain links to your website, as well as build trust and brand recognition with search traffic. If online audiences are paying attention to you because they trust your opinion, they are more likely to trust your website and products or services.
Without relevant content on your website, there is no reason for users to stick around, so you are likely to get a high bounce rate. It will also make it less likely that Google will rank your site well in search results. You should therefore make sure that every page on your website serves its purpose for anyone searching for that information online, by targeting the content to your most valuable keywords.
Whether it is a page on your website that offers a service, a product page on an eCommerce website, or a blog article, the content matters. As well as being unique from any other page, it should explain, inform, and be relevant. Some SEO experts could argue that volume is important too, and I agree to some extent – but writing 3,000 words for the sake of it is probably just a waste of time. First and foremost, the content always needs to be relevant and informative, so my opinion is that quality is more important than quantity.
You can use blogs to start conversations with your traffic, and to build your brand by talking about topics relevant to your industry in an interesting and informative way. You can also use them to build internal links to key transactional pages on your site, or to provide inspiration around how users can benefit from your products and services, in an engaging way which isn’t too salesy. Look at your competitors and see what type of blogs they’re creating. Monitor your analytics and find out which type of content resonates most with your site traffic. Also look at which different types of blogs get more or less social shares or comments.
Ensuring that your website performs well is vital in terms of search visibility. Improving code, image compression, and server setup are among the most important aspects of SEO.
Google has stated that they will rank mobile-friendly, faster-loading websites higher than those which don’t provide a good user experience in these areas. So if you have a slow website, or it doesn't work on mobile, then you need to address these two issues as soon as possible.
There are numerous techniques you can look to for helping your pages to perform well in website speed tests, including:
It's advised to use a content distribution network (CDN) to optimise site performance, helping you to deliver the best possible experience for users landing on and interacting with your site.
Meta data sits within the HTML of your website pages, passing on information about each page’s content as it is crawled by search engines. You can create meta tags within your website’s CMS to help boost your SEO performance. These tags are snippets of text which are invisible to users, but will describe key elements of content within your pages. Your meta tags should incorporate your target keywords.
The most important meta tags for SEO are:
You can also set social data for each page, which enables you to show specific text and image content when users share your content in social platforms, such as Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and even WhatsApp.
Keyword research is a core SEO task that involves identifying popular words and phrases which users enter into search engines. Understanding what your users are searching for helps you to better serve their needs with your content. You can optimise everything you write with these terms, as much as possible while still sounding natural and written for humans, not search engines (otherwise you’ll be penalised by Google for keyword stuffing and by not sounding like a true and trustworthy authority). You can optimise your meta data to target your keywords too.
Research the keywords that work best for your business, looking at a combination of insight:
Remember that keywords must always be relevant to your product or services, while the content must be of a high quality to rank well. So always follow up keyword research with effective content creation or optimisation of existing content, otherwise your investigative efforts will be wasted.
This is a technique that SEO agencies use to gain links to either your homepage or a chosen page on your website (this could be a product page or, ideally, a campaign landing page containing a creative asset or information key to the story, as journalists are more likely to link to this for free). Research is undertaken to present an idea, story or data set in a creative manner so that online coverage is earned within blogs, national press, social shares and other third-party content.
The primary objective of creative SEO campaigns is to boost website traffic and improve page authority, as well as overall domain authority. If the destination page is properly optimised for your target keywords, then these campaigns can also help to improve your search rankings too.
With the SEO industry growing and flooding the internet with competition, as well as online news constantly churning out new headlines, you are required to be increasingly creative to stand out online. It is becoming increasingly challenging to grab users’ attention as we spend more time online consuming ever-changing content, so it is worth prioritising strong, properly-planned creative SEO campaigns. They can only be successful with creatively-minded people working on them and high-quality assets which present something new (or refreshing in some way) and captivating for readers.
Many of the best creative SEO campaigns in the industry can end up going viral and making online news headlines. This has blurred the line between what used to be considered as strictly separate disciplines, using engaging news stories to improve website performance metrics.
Newsjacking requires imagination, reactivity, quick thinking and good contacts. It simply means giving your take (in the form of advice, opinions or data) on a current news story, in order to get your brand noticed for something many people will already be talking about. To do this, you’ll need to stay aware of what’s happening in the news every day – this could mean either stories making national headlines, or new developments in your industry.
If you can find something out about what’s happening in your industry before anyone else can (for example, by making a Freedom of Information request for unpublished data before it’s public knowledge), then you may have struck gold in terms of online coverage, ideally with authoritative sites linking back to you. This is because you can use the information to give journalists an exclusive story they wouldn’t have otherwise had.
One of the best ways of newsjacking, with minimal time input or cost, is to answer journo requests, which are published online before journalists write a story. This lets you get ahead of the news, so that what your brand puts out is as timely as possible, with minimal risk of your content dating and becoming irrelevant before it’s even gone live.
Journalists will put out journo request callouts on Twitter (using #journorequest or #prrequest), or through sites such as Help a Reporter Out (HARO), asking for information to inform and add value to their planned news stories. If you are an authority in your industry (or someone in your company is) and can quickly provide the useful information a journalist is looking for, supply a quote from an expert, or have a relevant case study, you have a good chance of being featured on their site. This all depends on your ability to supply the information by the required deadline, as journalists often have a pretty short turnaround to stay newsworthy.
Getting a backlink out of it isn’t always a guarantee, so it’s best to check with the journalist before supplying the information so that you can try to get the best possible value from the coverage (there’ll be little to no SEO uplift without a link).
As well as using creativity, it is still crucial to make your website 100% SEO-friendly in terms of technical and website development. Search engines like Google like websites that don't have bugs or 404s, errors or too many redirects. Keeping on top of your technical SEO is one of the most important areas of activity you should focus on, as it provides a strong foundation for all of your content to sit on, helping to drive organic performance and good user experience.
Your site should have regular technical SEO audits scheduled as part of BAU to ensure that everything is running properly. Fixes can then be scheduled accordingly for any flagged issues. So how do you decide which tech SEO errors should be prioritised? Look at the value of carrying out this work to your overall SEO performance. What impact will it have on organic traffic?
Critical technical SEO issues, which are usually worth addressing as soon as they appear, include:
There are situations where you should 301 redirect your 404 errors (which occur when a page you're sent to from a URL no longer exists), and situations where you shouldn’t. In many cases, there can be good reasons for having 404 errors on your site, with redirects sometimes being the most effective method of dealing with them.
For example, another site may have attempted to link to your site but made a mistake in the URL they’ve entered – you'll need to resolve this by redirecting referral traffic to the correct place. However, you could also contact that site and ask them to correctly amend the URL within their CMS (if this doesn’t prove successful, the 301 is probably the way to go).
You may have also deleted a page on your site for one reason or another, in which case you’ll want visitors to your site to be served with alternative relevant content which serves their needs. If no other such page exists, then a 404 is fine as it’s the most relevant message for users to receive – better than redirecting them to content completely irrelevant to what they were looking for, as this will leave them confused and harm user experience.
However, you shouldn’t automatically 301 redirect every 404, as Google will still treat all of these pages as 404s, meaning that the pages won't pass value. Each 404 error should be assessed individually, with the best course of action differing for each one. 301 redirects should only be used if they are sending users to the most relevant content which benefits their user experience.
Many people think that having any 404 errors in their site profile will automatically be viewed negatively by Google, however it’s fine to have some here and there – they're a normal part of the online ecosystem. As long as they’re also fixed accordingly as soon as they’re found, so that you can keep the numbers down as much as possible, you won’t lose SEO value just because 404s exist on your site. It’s far worse to try and hide them all from Google in an extreme and unnecessary attempt to avoid impacted SEO performance.
Creating a sitemap allows Google to understand what content sits on your website, and which pages should be prioritised in search. They may not always be necessary, as properly-linked pages on your website will still be discovered by Google. However, if your site is fairly new and doesn’t have many backlinks yet, then sitemaps can definitely be useful in helping Google to find your pages. Conversely, sitemaps can also be useful if your site is huge, with a very high volume of pages, as Google is likely to struggle finding content.
You can use plugins to help you create sitemaps, which vary according to your CMS. You could also use a third-party tool. Either way, you should still review your sitemap manually to ensure that it includes all of the pages you’d intended it to.
You can submit your sitemap to Google using Google Search Console (you’ll find ‘Sitemaps’ under ‘Index’ in the left-hand menu). You’ll need to correctly enter the exact URL which your sitemap sits on (it'll usually look something like site.com/sitemap.xml, which varies according to how you created it). Once it’s been submitted, you’ll be able to spot errors such as duplicate URLs, which you may not want to be indexed in search. In this case, you can remove them from your sitemap.
As well as producing detailed reports on organic results, there are various ways you can use Google Analytics for enhancing SEO. This popular tool allows you to uncover many key areas of insight, using your findings to inform your list of priority tasks and even whole strategies, ultimately improving your site’s performance in search.
Here are a few methods you can employ to use Google Analytics for improving SEO:
While many tools can assist with your SEO activity, Google Search Console stands out as it can cover the majority of your tracking needs around keyword rankings and SEO. It also provides endless useful information which you can harness to stay at the top of your game in terms of SEO performance. You can connect it to your Google Analytics account too, which brings a range of other benefits in terms of extra insight.
Here are a few ways you can use Google Search Console to improve your SEO:
While social media is commonly used as part of content marketing, its influence on SEO performance is often debated, with no clear-cut answer. Although pages on social platforms can be crawled by search engines, there’s no way of knowing whether these pages contribute to your organic rankings.
However, bringing social media into your SEO activity can certainly help your performance indirectly. Building social engagement through high-quality content is all part of good brand building online - once you have a positive relationship with these audiences, it boosts your chances of those users clicking through to visit your site. This can result in an increased domain authority, more backlinks and other positive metrics which can end up influencing your organic rankings.
You should always use social media to amplify the content you create. It won’t get seen just by sitting there, so just as you would optimise the content for search and outreach it to external sites for backlinks, you should place it on your social platforms to increase the chances of users landing on your site. You can tempt social users to click through to your onsite content by including short, appealing snippets on social posts which leave them wanting more.
When it comes to video, Google holds this type of content in high regard. It will crawl any videos you host on YouTube to include in organic search results, so that your social content can end up ranking – make sure it’s well optimised for SEO within the meta data boxes. You should include links to your site within your video page too - remember that YouTube is a huge search engine of its own, with billions of viewers, so don’t waste that opportunity.
SEO and PPC are like night and day. So when you ask what is seo? Which part of SEO are you talking about? SEO is based on strictly ‘free’ activity, which has the ultimate aim of performing well in organic search results and attracting traffic naturally (which is why it’s known as ‘organic’). You have to ensure that anything you do follows the rules of what search engines will look at positively (even when these aren’t exactly clear, as with Google’s infamously mysterious algorithm updates), and results won’t occur overnight – in fact, they could take up to a few months to materialise. The benefit is that once you’ve figured out your strategy and attracted organic traffic by ranking for your target keywords, your ranking pages won’t require constant attention to maintain this traffic. It can also prove to be cheaper in the long-term, as keywords are never bought, instead being ranked for through the efforts of an often modestly-sized team, which may form only part of their overall activity.
Pay-per-click (PPC) is all about appearing in the ads at the top of the search results, by paying for clicks to your site. It is fast-acting - as soon as you start a campaign in your chosen platform, which doesn’t take long at all, you will see results much more quickly than you would with SEO. This quick turnaround allows you to rapidly figure out what does and doesn’t work best for you in attracting results. You can also target very specific demographics with your PPC posts, so that they only attract highly relevant traffic to your site. However, depending on your industry, PPC can become pretty expensive. The more competitive your industry, the more expensive the keywords will be to bid on. They also become less effective over time, as the effect of your ads start to wear off on people when they become bored with seeing them. This is the opposite of SEO (when it’s done well), where you attract loyal and valuable traffic by repeatedly serving them with engaging content over time and earning their trust.
There are various pros and cons to each discipline, but most successful businesses don’t have to choose between SEO and PPC – they incorporate both into their marketing strategies. Why not reap the benefits of them both?
In short, it depends on the nature of the activity and the work required to deliver results for your website. Factors which will need to be taken into account include your current position in the market, the quality and age of your website, the size and quality of your competitors and the difficulty of the search terms you’ll be targeting.
So there's no definitive guide to SEO service costs from agencies. If you're a startup brand and have limited funds, we recommend that you work out a sustainable monthly spend, which is realistic for you as a business. Do you know how much you could afford to spend per month for 12 months minimum? If you're an established business, we would advise that you give your SEO agency a guide figure within a price range. This way, they can propose two different strategies, with one being more aggressive so that you can see the difference. You can then compare and make an informed decision based on their proposal.
What we would always say is that SEO should definitely be part of every marketing budget, so it should be a lifetime spend. Organic SEO strategies shouldn't be turned on and off; they should be consistent. Different types of tasks can be executed, with various SEO strategies explored, but while these can change, overall SEO activity should never stop. Google likes consistency, and the more SEO work you do, the better your results will be.
We'd also recommend only adopting SEO strategies that are likely to get results. There's no point in paying for SEO if it doesn't work, or if your budget isn't big enough – agencies should be honest with you about this from the start. Make sure the SEO agency understands what you can afford, and in turn, you understand what is achievable within that.
If you don't know what your SEO budget is, talk to your SEO agency and communicate openly. It's a waste of time if the agency jumps ahead and spend valuable time creating an SEO proposal that will get you amazing results, but costs too much for you. You also don’t want to waste your own time communicating on a proposal that you'll never be able to take up.
Absolutely not. Do not believe anybody who says that Wordpress is the best CMS for SEO. In fact, don't believe any person who states one particular CMS is better for SEO. Because the truth is, it doesn't matter which CMS it is, as long as it allows you to manage essential data. These include entering unique meta data on every page, incorporating global meta data, global SEO settings and automations. Your CMS should also allow you to easily manage on-page content, including text, images and video, and create page redirects. Changing alt text is another task you’ll want to easily carry out when needed. All of these are simple tasks and should come as standard with a CMS. We know for sure that these are build into Craft CMS, which is our preferred choice of content management system.
So as long as your CMS gives you the ability to do the above, it ticks the box in terms of SEO. However, even if your CMS does give you those abilities, it doesn't mean your site is SEO-friendly until you cover all of the essential elements of SEO explored in this article. If, for example, you enter meta data incorrectly, fail to optimise page content, or upload the wrong file sizes for images, that's not the fault of your CMS. It's down to you to ensure that your SEO performance is as strong as possible.
In our eyes, every SEO campaign needs a strategy, starting with your biggest priority being executed before anything else. You can't do everything at once, because Google will see this as spam. So that's why a carefully-planned SEO strategy is very important, to create a hierarchy of tasks to prioritise accordingly.
Whether you're a startup or an established brand, SEO should be part of your marketing budget. Be consistent in your efforts and, crucially, make sure you trust your SEO agency. Pick an agency with proven results and somebody who can communicate what they are going to do in simple terms. Communication is key because if you don't understand technical SEO, it's the agency’s job to help you understand.
We always advise that you hire the SEO experts to do this work BUT if you're going to give SEO a go yourself, on your own brand. Then we advise working with an agency who understands this process, therefore you can have the help and guidance from an agency to steer you in the right direction. Being open and honest is the best thing for your brand, rather than giving it a go yourself and making more harm than good in terms of SEO. We'd also advise you deal with somebody who speaks your language, as communication is vitally important - so if you speak english, hire an english speaking SEO expert.
If you're still reading this article and you'd like to discuss a super SEO project then feel free to get in touch to speak to our agency founder, Andy, today.
Co-Founder of MadeByShape. Most of my blogs are about business related aspects, not just web design.